J.P. Morgan: What Will the Recovery Look Like From the COVID-19 Recession?
Prospects for a quick, V-shaped recovery compared to a slower, U-shaped rebound in economies and markets post-COVID-19, as confirmed cases worldwide top 1 million, central banks unleash unprecedented stimulus and jobless claims soar.
V-Shaped or U-Shaped?
Best case scenario V-shaped recoveries, or those that start with a steep fall, but trough and recover quickly, have been more common in growth and corporate profits than in financial markets over the past 50 years.
“If recoveries are equal to recessions in duration and magnitude, then the output lost in the downturn will be fully recouped during the rebound and asset markets might retrace as quickly as they slumped. Hence, the always hoped for and almost always delivered V-shaped profile. If the recession inflicts longer-term damage to balance sheets or labor markets, then the recovery of lost income will be slower and so might be the rebound in corporate profits and asset prices. Hence, the dreaded U,” said John Normand, Head of Cross Asset Fundamental Strategy at J.P. Morgan.
The debate between a V or U-shaped recovery
Number of monthly news stories mentioning either V or U-shaped recoveries in the economy or in markets
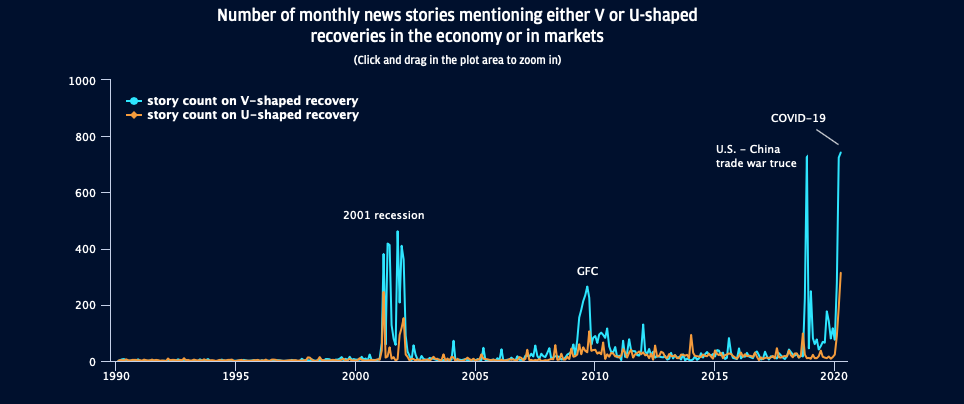
“The COVID-19 recession might only be one or two months old, but a few signs of the always hoped for V-shaped recovery are starting to emerge,” said Normand.
Firstly, in markets, assets that central banks are buying directly and in size, such as the Federal Reserve’s unlimited purchase of U.S. Treasuries, mortgage backed securities, and municipal bonds have already retraced about half their crisis losses. U.S. high grade corporate debt and U.S. equities have recovered one-third of this year’s sell-off.
Similarly, implied volatility has faded by half, in markets where quantitative easing (QE) programs are overwhelming, while volatility has been stickier in markets where there has been no direct support, such as other global equity markets, oil, and emerging market (EM) currencies.
Outside of markets, in recent activity data, purchasing managers index (PMIs) for the country at the leading edge of the pandemic – China – showed manufacturing and services output expanded in March, as outsized as its collapse in February.
Chinese PMIs led on the downside and could lead on the upside
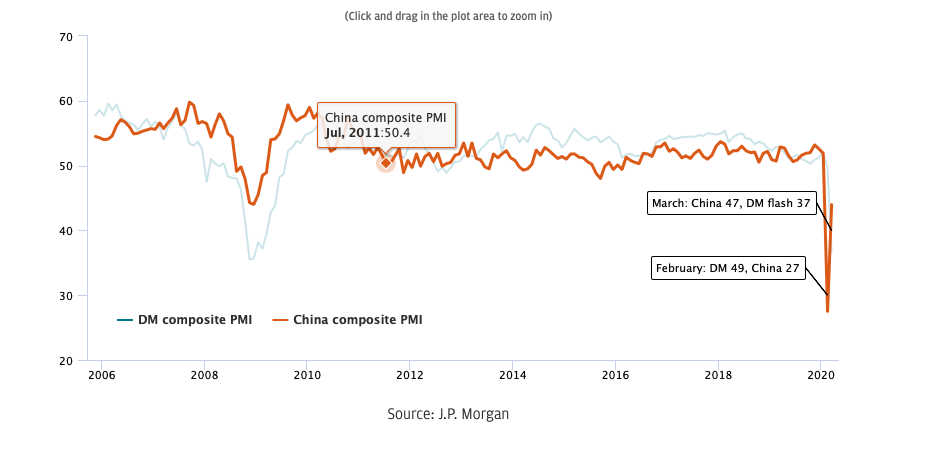
Source: J.P. Morgan
If China is COVID-19’s “first-in first-out” economy, then other countries such as Italy, the rest of Europe and the U.S. could follow from May as they repeat the sequence of lockdown, monetary and fiscal stimulus, relaxation of lockdowns then gradual normalization of activity.
Lessons from Previous Recessions and Outlook for 2020 and 2021
Even though there are good reasons to be skeptical that other countries will follow China’s normalization path closely, it has stirred the debate of a V versus U-shaped recovery in economies and markets – a familiar topic from every recession. For growth, V-shaped patterns have emerged after six of the past seven recessions, meaning that real GDP recovered to its pre-recession level in the same number of months or fewer than the recession’s duration.
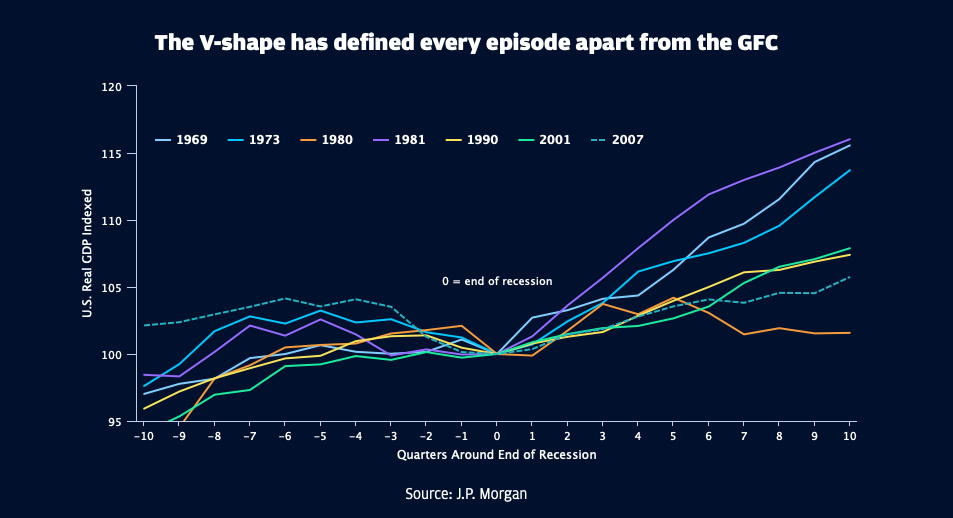
Where recessions have persisted for a year on average, only nine months were required to return to the previous level of output. The exception was the post-global financial crisis (GFC) experience, which lasted for 18 months but required 21 months to return real GDP to its pre-crisis level. The jobs recovery post-GFC took even longer. About six years were required to return the unemployment rate to its pre-crisis level, so about three times as long as the recession itself.
The pattern in U.S. corporate profits recovery has been less uniform. Although, on average, corporate profits returned to their pre-recession peak in about the same number of months as each recessions’ duration, there are two outliers.
The 1980 recession triggered by the oil shock of 1979 was followed by a second recession in 1981, so there was no recovery in profits for several years. The post-GFC experience was the opposite: despite an anemic growth recovery over a few years, corporate profitability returned to its pre-GFC highs within 12 months.
There are other, grimmer possibilities like the L-path for an economy that doesn’t recover for years, such as the Great Depression or the W-swing for a double-dip recession, similar to what took place in the U.S. in the 1980s or how in Europe, the sovereign debt crisis followed the global financial crisis.
Despite the V-shaped pattern often seen in growth and corporate profits, the typical path of asset prices cannot be summarized in a single letter. Equities, for example, have required 20 months on average to recoup their peak-to-trough recession losses, but with a wide range.
Four of the stock market recoveries following recessions in the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s occurred in only a few months, whereas those that followed bubbles in the late 1990s, in ”dotcom” stocks or in housing in the mid-2000s, required about four years to retrace.
Full retracement in credit spreads, or the difference in yield between a U.S. Treasury bond and another debt security of the same maturity but different credit quality, has also required more time on average, around 18 months, than the recovery in the underlying economy.
“The U.S and global economy might exhibit more U than V-shaped characteristics as occurred after the GFC, so will likely fail to recoup its 2020 first half output loss even by the end of 2021. Does growth normalization that requires at least six quarters imply that markets will need another 18 months to retrace fully their first quarter 2020 losses? No. The retracement process can be shorter in markets with direct policy backstops,” said Normand.
“Even markets that mirror the economy’s U-shaped path are nonetheless in a bottoming-out process with an upward bias over time. These deserve neutral allocations at worst and more likely small over-weights given the risk/reward when the economy turns,” added Normand.














